Robotic Motion Learning Framework to Promote Social Engagement
2017
Master Thesis
hi
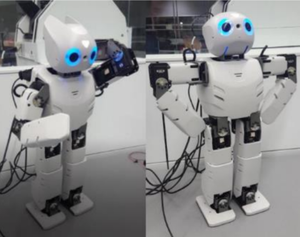
This paper discusses a novel framework designed to increase human-robot interaction through robotic imitation of the user's gestures. The set up consists of a humanoid robotic agent that socializes with and play games with the user. For the experimental group, the robot also imitates one of the user's novel gestures during a play session. We hypothesize that the robot's use of imitation will increase the user's openness towards engaging with the robot. Preliminary results from a pilot study of 12 subjects are promising in that post-imitation, experimental subjects displayed a more positive emotional state, had higher instances of mood contagion towards the robot, and interpreted the robot to have a higher level of autonomy than their control group counterparts. These results point to an increased user interest in engagement fueled by personalized imitation during interaction.
| Author(s): | Rachael Burns |
| Year: | 2017 |
| Month: | August |
| Department(s): | Haptic Intelligence |
| Bibtex Type: | Master Thesis (mastersthesis) |
| School: | The George Washington University |
| Degree Type: | Master of Science |
| Language: | English |
| URL: | https://search.proquest.com/docview/1953256291?pq-origsite=gscholar |
|
BibTex @mastersthesis{Burns_2017_MotionLearning,
title = {Robotic Motion Learning Framework to Promote Social Engagement},
author = {Burns, Rachael},
school = {The George Washington University},
month = aug,
year = {2017},
doi = {},
url = {https://search.proquest.com/docview/1953256291?pq-origsite=gscholar},
month_numeric = {8}
}
|
|